This is the first video of our “Vianeo method” MOOC. It is available to people attending the Vianeo Certification in order to coach innovators.
In this video, you will find out why effectuation, Design Thinking and Lean startup are
complementary in the use of the Vianeo method and their importance
in the life of entrepreneurs.
- To understand the coach position
- To accept uncertainty
- To make the entrepreneur decision-making process easier
MOOC program
- Principe 1 : “un tiens vaut mieux que deux tu l’auras”
- Principe 2 : raisonner en “perte acceptable”
- Principe 3 : le “patchwork fou”
- Principe 4 : la limonade
- Principe 5 : le pilote dans l’avion
Design thinking
Lean startup
Sources
Introduction
Before getting straight to the point and discovering the methodological approach of the coach, who allows the innovator to solve his enigma, it is important to be sure you have the right posture.
Posture of the coach
This posture should help you accept the fact that you don’t know more than your project leader, where it is heading. I would like to stress this point because it is essential, “No more than the project leader, you do not know where it is heading”!
Uncertainty in innovation
But be reassured that this uncertain situation is not worrying! It is a fact to be accepted! And once accepted, it is also good news!
It’s good news because everything is possible under uncertainty! And this is something the entrepreneur is fully aware of, which is why he is committed to this approach! Don’t tell him he’s going to fail, he can’t see it!
No, he’s not unconscious. On the opposite, it is very rational. And to do so, he more or less consciously uses approaches that have proved their worth in the world of entrepreneurship, Effectuation, Design Thinking and Lean Start-up.

Innovation approaches
These three approaches allow uncertainty to be handled with serenity and confidence. Uncertainty brings opportunities.
These three approaches are very complementary, we will come back to their definitions and added value in this video.
Each one brings concrete and operational support during the life of the project to keep the project on track while the fog has not yet lifted offshore.
Effectuation
Effectuation is a strong word, not easy to understand at first, and yet it is something you have always done. Indeed, you have always acted in line with your means and resources, these have generated effects (hence the term “effectuation”) which have themselves become new means for you. So your life has been shaped, with its share of surprises and phases of adaptation and construction.
An entrepreneurial project is above all a life story. The project leader enters into an adventure motivated by vision and conviction, but doesn’t know exactly what is going to happen. Effectuation illustrates the entrepreneur’s skill in “dealing with” it. A very effective capacity in the face of uncertainty.
Sara Sarasvathy, who theorized this approach, identified the 5 principles that are specific to this entrepreneurial posture. I will only mention them briefly and I suggest that you consult the bibliographical references and additional resources at your disposal.
Principle 1 : “a bird in hand is worth two in the bush”

This principle consists in being aware of the means and resources at your disposal and progressing with your means instead of wanting what you don’t have now. In an uncertain situation, there is no guarantee that we can have what we don’t, and there is no guarantee that this is what we will need to move forward with the project.
“Doing with your means” allows you to stay anchored in reality and always progress, while “wanting what you don’t have” is a dream, very likely never to come true and thus can lead to a bitter failure.
Let’s take a simple example to explain this: “you’re coming home from a long day at work, you’re hungry, how are you preparing your dinner? You have two options, either open a recipe book and strictly follow the instructions, or open your fridge and create a recipe based on the ingredients you find there. In the first case you pre-establish the goal to be reached, which is only possible if you have all the ingredients. In the second case “you do with what you have” and you will reach your goal which was to eat. And in addition, you may be nicely surprised by the final result!
Principle 2 : reasoning in “acceptable loss”
Principle 2 of effectuation is called “Reasoning in Acceptable Loss”: rather than reasoning in gain, a totally fanciful prediction at the start-up stage of a project, project leader think in terms of acceptable cost and loss. This loss can be measured quantitatively but also in terms of family value, level of social recognition, time spent…

Principle 3 : the “crazy patchwork”
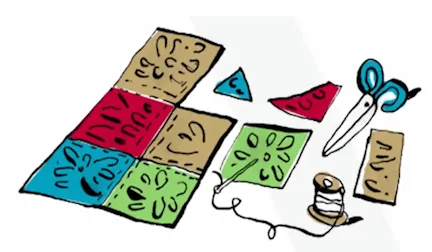
Principle 3 is the “crazy patchwork”: the project is built from the combination of parts provided by the involvement of stakeholders. These parts have not been predefined to be connected and yet they constitute an aesthetic and understandable complete picture. It is the principle called co-conception.
Principle 4 : “lemonade”
Principle 4 is called ‘Lemonade”: be open to surprise, as the English saying goes, “when life gives you lemons, make lemonade”. In other words, learn from a situation at a given moment to find new and promising opportunities. As Edison said: “I have not failed. I’ve just found 10,000 ways that won’t work.”
Principle 5 : the “pilot in the place”
Principle 5 is called “Pilot in the place”, shows that instead of trying to predict the future, you’d better control the present and transform it so that your vision can actually happen.
Now enjoy finding in your own projects examples of the application of these 5 principles, You will see that they are many!

Design thinking
Design-thinking was born in the heart of the Sillicon Valley around Stanford University.
“Design thinking is a science that uses the sensitivity, tools and methods of designers to enable multidisciplinary teams to innovate by matching user expectations, technological feasibility and economic viability”.
Design-thinking is a process that promotes the connection between various environments to highlight the real needs in a given situation, the reality of problems and thus help to find adapted solutions that make sense. The important thing is the ability to do, even if the optimal solution is not immediately achieved.
Used in an innovative project, in an uncertain context, design thinking favours market exploration and a detailed understanding of needs to better define an appropriate offer.

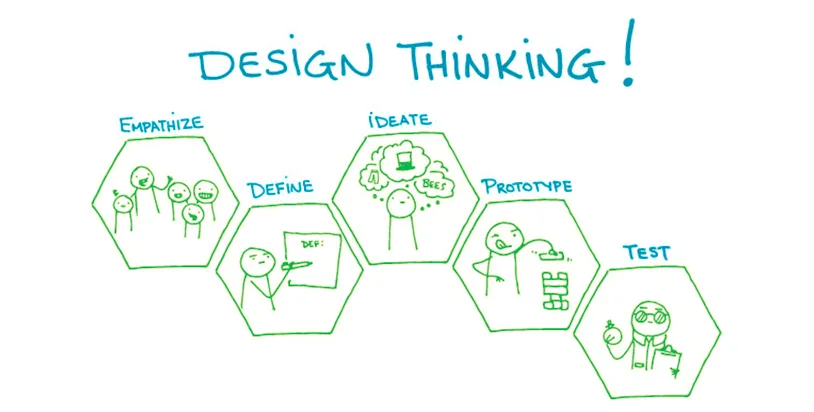
Lean Startup
It was made one of the fundamental approaches to entrepreneurship by Eric Ries in his book The Lean Startup.
The principle of Lean start-up is based on the need to validate in the reality of a new use. The approach is based on the principle of permanent trial and error to ensure the development of a solution focused on meeting needs first and foremost.
Lean start-up has given life to a tool often used in the world of start-ups, Lean Canvas. It’s one of the supports commonly used to represent the business model of the project, obtained at the end of the questioning process that we suggest to you.
So, we have just quickly seen effectuation, design thinking and lean start-up, 3 essential methods that will allow you to deal with uncertainty with confidence. They will bring you pragmatism, realism and serenity in the exploratory work that you are carrying out with each project leader.
Sources
- TED X : SARAH Sarasvathy
- Randerson, Kathleen; Fayolle, Alain (2013). “Business emergence”.In Carayannis, Elias G.
Encyclopedia of Creativity, Invention, Innovation and Entrepreneurship. New York: Springer. pp. 156–159. ISBN 978-1461438571. Retrieved 9 November 2014.
- Sarasvathy, Saras D. (2009). Effectuation: Elements of Entrepreneurial Expertise. Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing. ISBN 978-1848445727.
- Dos Santos, Ricardo. Essay on Effectuation
- The Lean start-up – Eric Ries
©Vianeo
